Table of Contents
Parents are constantly striving to keep their children safe and healthy. From protecting them from illnesses and bullying to preventing injuries when playing, moms and dads go to great lengths to shield their children from harm. However, one critical area sometimes slips under the radar: car seat safety.
Car seat safety is an important precaution that helps protect children and should be considered by every parent. Data shows that car seats help in reducing the risk of fatal injuries for young children in vehicles. In passenger cars, they lower the risk by 71% for infants and 54% for toddlers aged 1 to 4. Car seats cut injury risks by 58% for infants and 59% for toddlers in light trucks.
In the United States, Child Passenger Safety Week is observed every September to encourage caregivers to double-check the selection, installation, and fit of car seats. To support that goal, this guide was created by Arash Law, a well-regarded California personal injury firm, using widely accepted traffic safety and pediatric recommendations. It is educational only and not legal advice, and agencies and community organizations are welcome to reference or share it to help families use car seats correctly.
Why Car Seat Safety For Kids Matters
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) reported that out of 42,514 traffic deaths in the U.S. in 2022, 1,129 (or 3%) were children under 14. Additionally, 156,502 children were injured. While these numbers represented a 6% and 4% decrease from 2021, respectively, the sobering fact is that, on average, three children lost their lives, and roughly 429 got injured in car accidents every day.
In 2022, among the 25,420 car occupants who lost their lives in road accidents, 3% (756) were children. Restraint system usage was documented for 675 of them. Of these, 39% (266 children) were not wearing a seatbelt. Equally alarming is the fact that 68% of children who died while riding with unrestrained drivers were also unrestrained themselves. The National Safety Council also highlighted this issue, noting that of the 555 child passengers under 13 who lost their lives in traffic accidents in 2023, 190 were unrestrained. Many others lacked proper restraints.
These statistics underscore the critical importance of using proper restraints for children in vehicles. While laws on child passenger restraints vary across states, they all require children to travel in age- and size-appropriate restraints until they can properly fit in adult seatbelts.
For example, according to child passenger safety laws in California:
- Children under age 2 must be properly restrained in a rear-facing child seat in the back seat of a vehicle.
- Children who weigh 40 pounds or more or are at least 40 inches tall are exempt.
- Children who are eight years old or have reached a height of at least 4 feet 9 inches may use a booster seat, but should not be forced to do so until they are ready. They must also properly buckle their seatbelts.
- Kids under 8 must sit in a booster seat in the car. All children under 13 should sit in the back.
Despite these regulations, the number of children who die or are injured in car accidents every day is staggering. In the majority of cases, parents or caregivers did not install or use child seats correctly. A study by Safe Kids Worldwide found that 4 out of 5 parents removed their children from booster seats too soon, before they were old enough or big enough for a seat belt. Three out of four parents do not know that children must ride in booster seats until they are at least 4 feet 9 inches tall, putting them at risk of serious or even fatal injury.
Parents and caregivers must use car safety seats properly to keep children safe. However, with so many options available, many parents find this confusing. It is possible to get help. The following tips can help you determine which car seat is right for your child.
RELATED: The Ultimate Guide For Pregnant Women Who Are Involved in Car Accidents (2020 Edition)
Child Car Seat Safety Tips All Parents Should Know
Before buying a car seat for your kids, keep in mind that not all car seats are the same. So, it’s crucial that you thoroughly understand the importance of knowing the right car seat for your child. When buying and installing a new child safety seat, consider the following checklist:
- Learn About the Four Types of Car Seats — There are many car seats for kids, but you only need to know four major types: rear-facing, front-facing, booster, and seatbelts.
- Check Seat Compliance With Safety Standards — A sticker on the side of the car seat confirms whether it meets Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
- See Whether Your Child Meets Height and Weight Requirements — The height and weight ratings are directly on the car seat and packaging.
- Check That the Harness Is Easy to Adjust — Practice adjusting the straps to see if they’re easy to maneuver, because you’ll have to adjust them many times every time your child rides in the car seat.
- The Car Seat Is Easy for You to Install — In addition to your child’s age, size, and developmental needs, the type of seat your child needs depends on several other factors, including how easy it is to install and remove. The NHTSA offers an installation guide on its car seat website.
- Have Your Car Seat Inspected — Visit a nearby car seat inspection station for assistance in installing a car seat or if you have recently installed one. Qualified technicians will check your car seat for free and even demonstrate how to use and install it properly. Virtual inspections are also available at some locations.
- Register Your Car Seat — Register the car seat with the manufacturer to receive safety updates and recall notices. Use the card provided or register on their website. If you face any issues, contact the NHTSA for assistance.
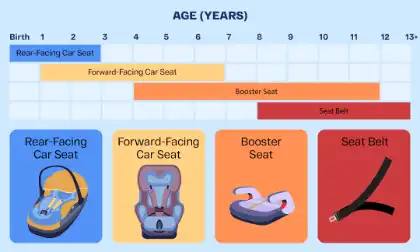
Different Types Of Car Seats
As children grow, their car seats must be updated to match their age, size, and developmental stage. Parents must understand the different types of car seats to maintain their child’s safety at every phase. There are four main types of car seats, each designed to provide optimal protection for specific age and weight ranges:
Rear-Facing Car Seats
Newborns face some of the highest risks of injury in a car accident. Infants are more susceptible to head and neck injuries due to their disproportionately large heads and underdeveloped neck muscles compared to older children. These injuries can cause serious consequences or even death. It is vital to provide your baby with every available protection whenever they are in the car.
Babies should use infant-only car seats until they are at least two years old. These seats are designed exclusively for newborns and small babies, rear-facing, and typically include a five-point harness for safety. Many models come with a detachable base, allowing parents to place the baby in the seat before putting the seat in the vehicle. Some infant and toddler car seats also include additional safety features for extra protection.
Rear-facing car seats provide strong protection for young children by supporting their necks and spines during a crash. While infant-only car seats must be rear-facing, convertible and all-in-one car seats allow children to stay rear-facing beyond infancy. These models accommodate toddlers as they grow, often up to 40–50 pounds, before transitioning to a forward-facing seat with a harness and tether. Keeping children rear-facing as long as possible is important for optimal safety.
Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Position shoulder straps at or below your baby’s shoulders.
- Check if the harness is snug, and you shouldn’t be able to pinch the strap.
- Straps should lie flat, with no sagging or twisting.
- Adjust the chest clip to the armpit level.
- Avoid placing blankets under or behind the harness.
- Dress your baby in thin layers, as bulky clothing can loosen the harness.
- Keep your baby’s head at least one inch below the top of the seat.
Front Or Forward-Facing Car Seats
Forward-facing car seats use harnesses and tethers to reduce forward movement in a crash. Children ages 4–7 should use a forward-facing seat with a harness and tether until they outgrow it.
Here are the different types of forward-facing car seats:
- Convertible Car Seat — Can switch from rear-facing to forward-facing. Keep rear-facing until at least age two or until your child reaches the seat’s weight/height limit.
- Combination Seat — Functions as a forward-facing car seat with a harness (for 40–65 lbs) and later converts to a booster seat by removing the harness.
- Travel Vests — An alternative for children 20–168 lbs, useful in cars with lap-only seat belts or for heavier children.
- Built-in Car Seats — Some vehicles have forward-facing child seats. Check the owner’s manual for height and weight limits.
The following tips can help you utilize front-facing car seats for your toddler:
- Move to a forward-facing seat only after outgrowing the rear-facing seat.
- Keep the harness snug with flat, untwisted straps.
- Position the chest clip at armpit level.
- Use the top tether strap, positioning it to the correct anchor point.
- If your child’s ears reach the top of the seat, they are too tall for it.
Booster Car Seats
Move your child to a booster seat once they outgrow their forward-facing car seat’s height or weight limit. However, they’re not ready for a seat belt alone until the belt fits properly.
A booster seat raises and positions a child so the seat belt fits correctly over the hips and chest, reducing the risk of injury in a crash. If the lap belt sits on the belly instead of the upper thighs, it can cause serious internal injuries in an accident. Here are the two types of booster seats:
- High-Back Booster — Provides head and neck support, ideal for cars without headrests.
- Backless Booster — Raises height for a proper belt fit but lacks head support, so it is suited for cars with headrests.
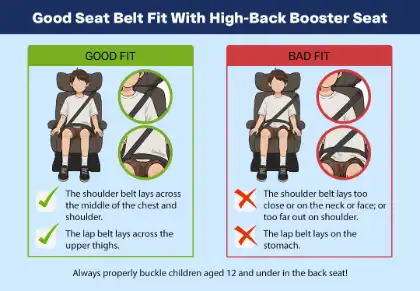
Belt-positioning booster seats can help prevent injuries in crashes when used correctly. Help keep your child safe with these booster seat safety tips:
- Use only booster seats that meet federal safety standards (check for a label stating compliance).
- Place the booster seat in the back seat and use both the lap and shoulder belts.
- The lap belt should rest low across the upper thighs, not on the belly.
- The shoulder belt should cross the center of the chest and shoulder, not the neck or face.
- Never tuck the shoulder belt behind the back or under the arm.
- Use booster seats with belt guides for a better fit if needed.
- If your car lacks rear shoulder belts, consider retrofitting seat belts or using a travel vest.
- Your child should sit back in the seat, with knees bent comfortably, without slouching.
- Let your child help choose their booster seat for comfort and engagement.
- Teach your child why a booster seat is important and how to buckle up properly.
Seat Belts
Keep your child in a booster seat until they can safely fit a seatbelt, because a proper fit provides protection in a crash. The lap belt should rest snugly on their upper thighs, not their stomach, to prevent serious abdominal injuries. The shoulder belt must cross the chest and shoulder, not the neck or face, for optimal safety. Finally, remember that the back seat is generally a safe place for your child to ride.
Is Your Child’s Car Seat Installed Correctly?
There are thousands of vehicles on the market and countless ways to install different car seats, making proper installation challenging. To help keep your child safe, have your car seat checked by a professional.
Free car seat inspection events are held periodically in many areas. At a car seat check, a certified Child Passenger Safety (CPS) technician will guide you through the proper installation and use of your child’s safety seat. Having a trained technician inspect your car seat can confirm correct installation, providing your child with additional protection.
When having your car seat checked, remember to bring the following:
- The vehicle your child will be riding in.
- Your child’s safety seat.
- The child safety seat manual.
- Your car owner’s manual.
- Your child (if possible).
Check your infant’s car seat safety at an inspection station or during a car seat check-up event. If you are unable to attend a car seat check, please reach out to a certified child passenger safety technician for assistance with your questions. Additionally, you can contact your state highway department, local police or fire department, or a hospital for non-emergency support.
For more information, visit the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration and Safe Kids Worldwide websites.
How To Spot A Counterfeit Car Seat
Unfortunately, a new and alarming issue is on the rise: counterfeit car seats. They pose serious risks, often lacking proper safety testing. Sellers market fake rear-facing seats as “3-in-1 Bassinet Travel Systems,” but these seats mimic approved models, fail crash tests, and pose serious safety risks.
Online marketplaces also sell unsafe knockoffs, like counterfeit Doona seats. Some lightweight harness “seats” and Chinese-made “booster seats” lack safety labels and fail crash tests, making them illegal and dangerous.
Counterfeit or unsafe car seats may not provide adequate protection for your child in a crash. In some cases, these dangerous products can give rise to product liability claims against the manufacturer or seller who put them on the market.
To help you verify if your child’s car seat is both safe and legal, we’ve put together a checklist of essential safety features, along with tips for verifying whether your car seat meets regulations. Not sure if your child’s car seat is authentic? Here’s what to watch out for:
- Manual & Registration Card — Authentic car seats include a manual and registration card, with manufacturer contact details and a logo. They are found on the seat or inside the box.
- Safety Labels — Legal U.S. car seats have specific labels, including a white label with red and black text that confirms they meet federal safety standards. Counterfeit seats lack these.
- Usage Labels — These labels provide details on reclining angles, belt guides, and weight limits, along with height and weight ranges in imperial or metric units.
- Manufacturing Information — U.S. car seats must display the model name, manufacturer’s details, production date, and place of manufacture in accordance with the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
- Certification & Recall Labels — Required statements include federal compliance, aircraft certification (if applicable), and a recall information hotline (1-888-327-4236 or www.NHTSA.gov).
- Label Placement — Label locations vary by brand and model, but are often on the seat.
- Seller — Buy from an authorized retailer. Check the manufacturer’s website for a list of approved sellers.
- Missing Parts — Harnessed car seats generally include a chest clip. If missing, the seat is likely counterfeit.
Why It’s Important To Rethink Buying A Second-Hand Car Seat
While most high-quality car seats can cost upwards of $500, purchasing a good one for your child shouldn’t be a financial burden. For budget-conscious parents, a well-selected second-hand car seat can be a practical choice.
However, avoid buying a used car seat from garage sales, flea markets, second-hand stores, or online sellers when you don’t know the previous owner or the seat’s full history. Avoid borrowing one from an unfamiliar source.
Before using a second-hand car seat, check the following:
- Crash History — Check if the seat has been in an accident.
- Recalls — Check the NHTSA website for recalls from the past 10 years.
- Expiration Date — Car seats should be less than six years old.
When installing the seat, read the vehicle owner’s manual and the car safety seat manual. Additionally, you can get professional assistance to confirm if you have installed your child’s car seat correctly.
Choosing A Car Seat For Your Child’s Safety
Car seats play an essential role in keeping your child safe while you are driving. When choosing a car seat for your child, their age, weight, and height should not be the only considerations.
Before buying, read reviews and check safety ratings. Besides being comfortable, the right car seat should have impressive features, be easy to install, and, more importantly, help keep your children safe when on the road.
Listed below are the car seats that have passed rigorous safety tests and meet federal standards:
- Doona Infant Car Seat & Latch Base Combination Seat — The Doona Infant Car Seat and LATCH Base feature a unique, patented, three-in-one design. According to Good Housekeeping, this car seat quickly and easily transforms from a car seat to a stroller, providing parents with a convenient way to transport their little ones.
- Graco 4Ever DLX Convertible Car Seat — The Graco 4Ever DLX 4-in-1 Car Seat gives you ten years of use. It easily transitions from rear-facing for infants to forward-facing for toddlers and then to a belt-positioning booster for children. The 6-position recline keeps your child comfortable, while the InRight™ LATCH system makes installation easy.
- Diono Monterey XT Latch Booster Seat — Good Housekeeping has featured the Diono Monterey XT LATCH Booster, a lightweight booster seat that provides your child with a comfortable ride. At 13.9 pounds, it is a portable seat suitable for kids ages 4–12. It measures 26.0 by 16.0 by 20.0 inches and also features a sturdy seatbelt and LATCH system to help maintain your child’s safety.
- BRITAX Boulevard ClickTight Anti-Rebound Bar Convertible Seat — The BRITAX Boulevard ClickTight Convertible Car Seat has two layers of side impact protection surrounding the head, neck, and torso. It features a 14-position adjustable harness and a quick-push recline, with a maximum weight capacity of 65 pounds.
- Chicco KeyFit 35 Infant Car Seat — The NY Times’ Wirecutter lists the KeyFit 35 among the choices to consider for 2025. The Chicco KeyFit 35 is a lightweight (8.5 lbs) infant car seat suitable for infants weighing 4 to 35 pounds and up to 32 inches tall. Its rear-facing-only design includes a European belt path for installation without a base, making it convenient for travel. It’s also an affordable, FAA-approved option for airplane use.
Common Car Seat Safety Mistakes & How To Avoid Them
We understand that installing a car seat can be challenging for parents. Here are common mistakes in car seat safety and tips to avoid them:
- Loose Installation — A car seat should not move more than an inch side-to-side or front-to-back. Wiggle the base to check, as a loose seat may not help protect your child in a crash.
- Incorrect Belt Path — Follow the car seat manual to check if the seat belt is routed properly. If the seat moves more than an inch, it’s too loose.
- Improper Shoulder Strap Position — For rear-facing seats, straps should be below the shoulders. For forward-facing, they should be at or above the shoulders. Adjust as your child grows.
- Loose Harness Straps — Pinch the harness at the shoulders — if you can grab extra webbing, it’s too loose. Tighten until snug.
- Chest Clip Misplacement — The chest clip should be centered at armpit level to keep straps in place.
- Ignoring the Top Tether — The top tether prevents excessive movement in a crash. Attach it to the designated anchor point.
- Wrong Seat Placement — The middle back seat is generally safe, but check your car’s manual for the best spot.
- Incorrect Seat Angle — A rear-facing seat tilted too upright can restrict breathing, while one that is too reclined reduces crash protection. Follow manufacturer guidelines.
- Wrong Seat Size — Choose a seat that fits your child’s age, weight, and height. Check NHTSA for guidelines.
- Expired or Crash-Damaged Seats — Don’t use a seat older than six years or one that’s been in a crash.
- Unsafe Accessories & Bulky Clothing — Aftermarket items and winter coats can affect harness fit and safety, so stick to manufacturer-approved accessories.
- Improper Cleaning — Harsh cleaners can weaken materials. Follow the manufacturer’s care instructions.
- Not Registering the Car Seat — Register with the manufacturer to get recall updates. Find local car seat checks for proper installation help.
Car Seat Injuries From Incorrect Car Seat Installation
Properly installed car seats are crucial for protecting children in the event of a crash. When installed incorrectly, they can put children at risk of serious injuries due to their smaller, more fragile bodies. Unfortunately, improper installation leads to many children suffering injuries in accidents.
In some collisions, injuries may also result from other faulty safety components, such as defective airbags. In these situations, attorneys experienced in defective airbag claims can investigate whether the manufacturer should be held responsible.
Here are some of the common injuries they may suffer:
- During a crash, an improperly installed car seat can cause a child’s head to hit the car’s interior or other objects, resulting in concussions or other traumatic brain injuries.
- Unsafe car seats can twist or bend a child’s spine during an accident, potentially causing spinal cord injuries and paralysis.
- With an improperly installed car seat, a child’s head and neck can violently jerk back and forth in a crash, resulting in whiplash and other neck injuries.
- In a car crash, a child’s body may get thrown forward, causing serious injuries such as broken ribs and punctured lungs.
- An unsafe car seat can lead to a child’s body being thrown forward in an accident, resulting in internal bleeding, burst organs, and other abdominal injuries.
Keeping Your Child Safe In The Car Seat
Proper car seat use is essential for protecting your child on the road. In the event of an accident, consult a lawyer experienced in traffic accident cases to understand your legal options.
Consider following these safety tips to help check if the car seat is properly installed and used correctly in all conditions.
- Always Buckle Up — Set a good example by wearing your seatbelt and confirming all passengers do the same. See that all caregivers are also using the proper car seat or seatbelt for your child.
- Adjust the Harness Properly — As your child grows, reposition shoulder straps and chest clips for a snug fit. If you can pinch the straps, tighten them. Bulky clothing can prevent a proper fit, so dress your child in thin layers.
- Keep Your Child Warm Safely — Instead of thick coats, dress your child in fitted layers like leggings, fleece jackets, and hats. Position the harness properly, then place a blanket or coat over it. Ponchos or zip-up jackets that flip forward also work well.
- Never Leave a Child Unattended — Unsupervised children can:
- Accidentally move the car into gear.
- Get trapped in the trunk.
- Suffer injuries from power windows, seat belts, or sunroofs.
- Experience heatstroke.
- Be backed over by a moving vehicle.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines — Refer to the car seat manual for installation and cleaning. If lost, contact the manufacturer (details are on the seat label). Avoid disinfectants, as they can weaken safety materials.
- Avoid Untested Accessories — Car seat covers, inserts, and other add-ons not included with the seat may reduce protection in a crash. Check if any additional items have Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) approval.
- Keep an Emergency Kit in the Car — Prepare for winter or unexpected stops by packing blankets, dry clothes, gloves, hats, and non-perishable snacks.
Car Safety Seats For Preemies And Babies With Medical Conditions
Premature babies and infants with medical conditions require extra care when traveling in a car seat. Before hospital discharge, doctors assess whether your baby can safely use a car seat for the ride home.
Hospitals conduct a car seat tolerance test to assess whether a baby can maintain normal heart rate, breathing, and oxygen levels while seated in a car seat. The test usually lasts 90 to 120 minutes or the length of the car ride home, whichever is longer. If your baby doesn’t pass, doctors may recommend a specialized car seat.
Who needs extra monitoring? The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) advises careful evaluation for:
- Preemies born before 37 weeks.
- Babies who struggle in a semi-reclined position (like a rear-facing seat).
- Infants at risk for breathing or oxygen issues, including those with Pierre Robin Sequence, a condition causing a small lower jaw, tongue displacement, and airway obstruction.
In some cases, doctors may recommend a home monitor to track breathing and heart rate. Following medical guidance offers a safe and smooth transition from hospital to home.
Car Seat Replacement And Insurance Coverage
If you were in a traffic accident, it’s essential to replace your car seat, even if you don’t think it’s damaged. When it comes to your child’s safety, it’s necessary to take precautions. They can be expensive, but many insurance companies cover the cost of replacing a car seat after an accident.
Check with your provider to confirm coverage and that they’ll cover the cost of a new seat. If you have trouble getting your insurer to honor this coverage, a car accident lawyer can explain your options and help you navigate the claims process.
Statistics About Child-Related Traffic Injuries
Traffic accidents are one of the major causes of death for children in the U.S. About 39% of the children who died in accidents weren’t wearing seat belts. On every trip, parents and caregivers should help keep children safe by properly putting them in the right car seat.
- Race, Ethnicity, and Children’s Safety in Cars — According to data compiled from 2015 to 2019, American Indian and Alaska Native children (2.67 per 100,000 population) had the highest child passenger death rates, followed by Black children (1.96). Additionally, 21% of Black, 15% of Hispanic, and 7% of White children aged 4–7 were unbuckled.
- Children’s Car Seat Safety in Rural Vs Urban Settings — From 2015 to 2019, child passenger deaths were more common in rural areas, with a rate of 4.5 per 100,000 people, compared to 0.9 in urban areas. Children in rural areas were also more likely to be unrestrained or in the wrong type of car seat, with a death rate of 2.9 per 100,000 versus 0.5 in urban areas. Additionally, car seat misuse was higher in rural areas (91%) than in urban areas (83%).
- Alcohol-Impaired Driving and the Use of Child Restraints — Drunk driving significantly endangers all road users, especially children. In 2021, 25% of child passenger deaths (ages 14 and younger) involved an alcohol-impaired driver. Among children killed in crashes, 43% were unrestrained when riding with a drunk driver, compared to 38% with a sober driver. Data shows that alcohol-impaired drivers are more likely to have unrestrained child passengers, with children under 2 being 2.2 times more likely to be unrestrained if the driver had been drinking.
Frequently Asked Questions About Car Seat Safety For Kids
Keeping your child safe in the car starts with proper car seat use. To help parents and caregivers make informed decisions, our accident lawyers have compiled answers to common questions about car seat safety.
What Is Considered A Safe Seat For A Child In The Car?
Recent studies continue to show that children are generally safer in the rear center seat when properly restrained. A 2023 study published in Future Transportation analyzed crash data and found that the second-row middle seat had significantly lower injury severity scores compared to other seating positions, reinforcing its status as the safest spot for child passengers.
How Long Should A Baby Stay In The Car Seat?
As a parent, it’s important to be mindful of the duration your infant or young child spends in a car seat. The common guideline for car seat use is the “2-hour rule,” which advises against keeping a baby in a car seat for more than two hours within a 24-hour period.
The rationale behind this guideline is that prolonged periods in a semi-upright position can place strain on a baby’s developing spine and may restrict airflow to the lungs, especially if the baby’s head falls forward during sleep.
For newborns, particularly those under four weeks old, some studies suggest limiting car seat use to 30 minutes at a time due to their increased vulnerability.
Why Can Winter Coats Be Dangerous In Car Seats?
Winter coats can be dangerous in car seats because they create a gap between the harness and the child’s body, making the straps too loose. In a crash, the coat can compress, increasing the risk that the child will slip out of the harness and suffer serious injuries. Instead, dress your child in thin, warm layers and use a blanket over the harness for added warmth.
Is It Safe To Use A Car Seat After An Accident?

The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration recommends replacing a car seat after a moderate or severe crash for the continued protection of your child. However, it’s not often necessary to replace car seats after minor accidents.
NHTSA considers a crash minor if it meets all of the following conditions:
- The vehicle could be driven away from the scene.
- The door nearest the car seat was not damaged.
- No passengers sustained injuries.
- The airbags did not deploy (if the vehicle has them).
- The car seat shows no visible damage.
If a crash does not meet all these criteria, replace the car seat promptly. Don’t use a car seat involved in a moderate or severe crash, and follow the manufacturer’s safety guidelines.
If your child’s car seat was involved in a moderate or severe accident, you may be eligible to seek compensation for a replacement and other losses. Many experienced car accident lawyers offer a free initial consultation. They can help you understand your options and assist you in seeking compensation.
Legal Guidance After An Accident
As a reminder, this page is educational and not legal advice. If someone is hurt, seek medical care, document what happened, and consider speaking with a licensed personal injury attorney about time limits and next steps with insurance. California residents can reach out to Arash Law for a free and confidential case review at (888) 488-1391.